Treatments
Lichen Sclerosus (LS)
It is a chronic inflammatory, non-infectious disease that is more common in women, especially during perimenopause, but it can also occur after early childhood.
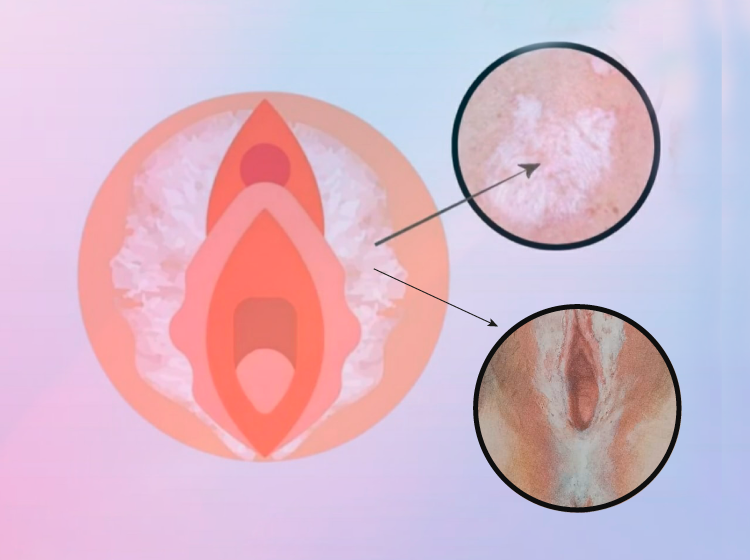
It affects the mucous membranes of various parts of the body.
It is a chronic inflammatory, non-infectious disease that is more common in women, especially during perimenopause, but it can also occur after early childhood. It affects the skin and mucous membranes of various parts of the body.
When it affects the genitals and perianal region, it can be highly debilitating due to the progressive atrophy of the skin, which can lead to significant tissue shrinkage, even narrowing the vulvar introitus.
Symptoms
If a woman notices discolored, wrinkled, or blotchy areas accompanied by itching, burning, or irritation, observes changes in the urinary outlet ("urethra"), or experiences painful sexual intercourse ("dyspareunia"), it is important to seek medical attention for a diagnosis and to initiate appropriate treatment.
Causes
The exact causes of Lichen Sclerosus are unknown, but it is likely a combination of factors such as an overactive immune system, genetic predisposition, local irritants, anxiety, and depression.
LS is not contagious and is not transmitted through sexual contact.
Diagnosis
It is confirmed through a small biopsy with local anesthesia in the doctor's office.
It is crucial to avoid delays in diagnosis, as early treatment can reduce or prevent anatomical changes in these women.
Treatment
With treatment, symptoms can improve or disappear. The treatment for LS depends on the severity of the symptoms and their location on the body.
Treatment can help relieve itching, improve the appearance of the skin, and reduce the risk of scarring and atrophy.
Even with successful treatment, symptoms may reappear, but without treatment, LS progresses to atrophy, adhesions, and stenosis, resulting in pain during sexual intercourse, including the inability to engage in it, urinary discomfort affecting sleep, rest, and the emotional well-being of patients.
The treatment of choice to start with is topical corticosteroids, such as 0.05% Clobetasol cream.
As a second-line treatment for patients resistant to Clobetasol, calcineurin inhibitors like 0.01% Tacrolimus are used.
Maintaining healthy skin with emollients and moisturizers is highly recommended.
For more advanced cases, regenerative and state-of-the-art treatments are recommended, such as:
- Hyaluronic Acid
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
- Gynecological laser
- Debridement of structures that have lost normal anatomy.
The treatment begins with vaginal laser therapy. The laser stimulates collagen regeneration and neo-vascularization.
This results in increased elasticity and lubrication of the vaginal canal.
Subsequently, the application of Hyaluronic Acid is performed because it acts as a potent hydrating agent, trapping intracellular water, leading to better hydrated and more functional tissues.
Platelet-Rich Plasma is used as a cell activator, providing great benefits for the patients.
After completing the treatment protocol, patients visit the doctor's office for maintenance sessions every 3 to 6 months in order to maintain the achieved results.
The procedures are outpatient, meaning they are performed in the doctor's office with painless local anesthesia cream.
They truly improve the quality of life.
